Habitats of Living Things
The Habitats of Living Things topic teaches students how living things stay safe, find food, and grow. All living things need the right place to meet their needs, and these places can look very different from one another. Some areas are hot and dry. Others are cold and icy. Many places are full of trees, while others are surrounded by water. Because each place has its own conditions, plants and animals must live where they can survive.
For example, some animals need plenty of water, while others can live with only a small amount. A cactus can stay alive with very little water, but many ocean animals cannot. Dolphins need deep water to swim, yet forest animals cannot live there. As students learn more about the environments where living things live, they begin to see why certain plants and animals appear in one place but not in another. This understanding also helps them notice how living things connect to the world around them.
What Are Habitats?
All living things—plants, animals, and even tiny insects—need a place to live. This special place where they can find food, water, shelter, and air is called a habitat.
A habitat is the home of a living thing. It provides everything the organism needs to survive.
For example:
- A fish lives in water because it can breathe through its gills and swim easily.
- A rabbit lives on land because it can run fast and hide in burrows to stay safe.
- A bird builds its nest in trees to protect its eggs and find food.
Why Habitats Are Important
Habitats are very important because they provide the basic needs of living things:
- Food – Plants and animals need food for energy.
- Water – Every living thing needs water to survive.
- Air – Air gives oxygen for breathing.
- Shelter – Habitats give protection from enemies and bad weather.
- Space – Living things need space to grow and move around.
Without their habitats, living things cannot live for long. That’s why it’s important to take care of the environment where they live.
Types of Habitats
There are many types of habitats on Earth. Each one is different in temperature, weather, and the kind of living things that live there. Let’s explore some common habitats!
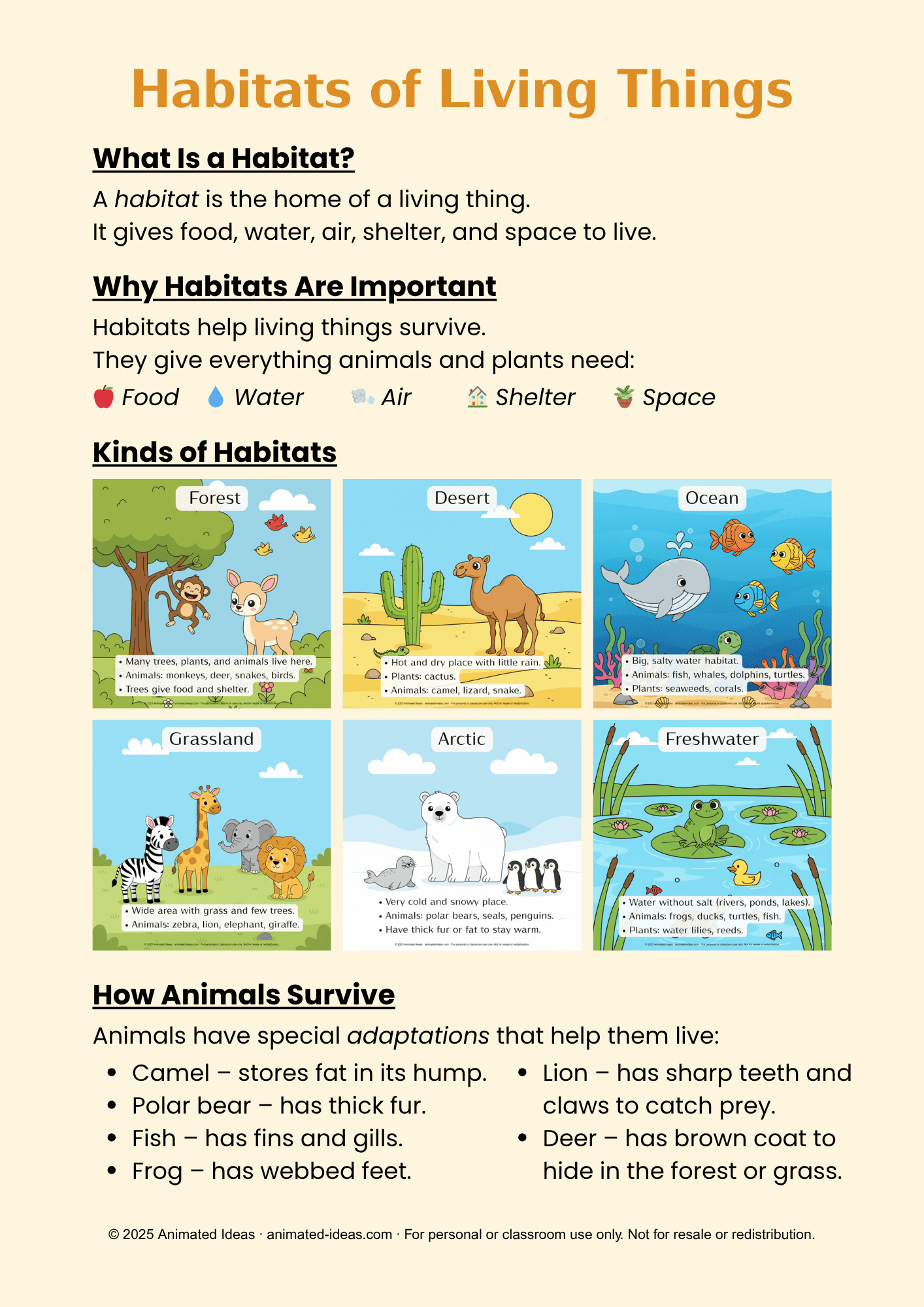
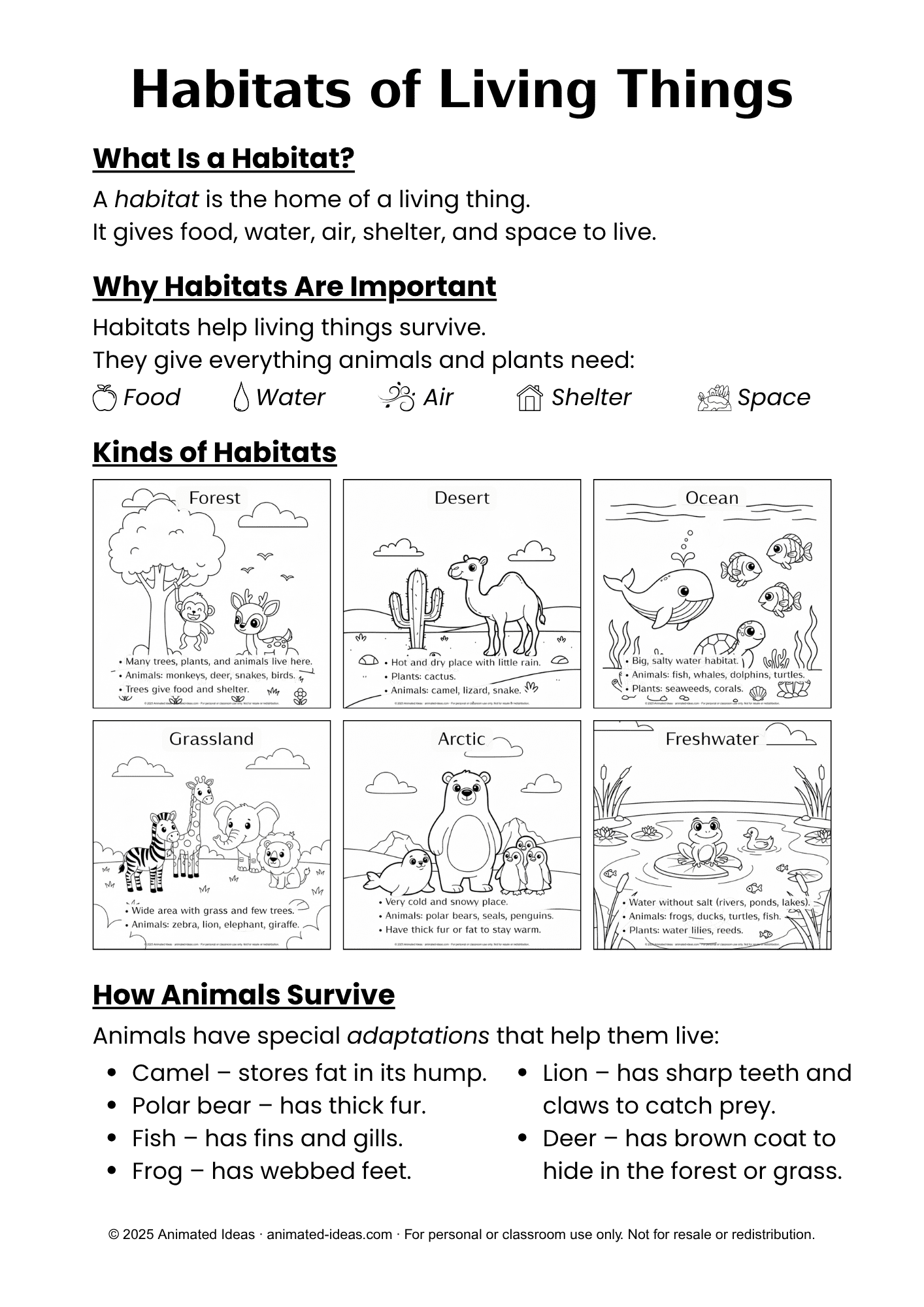
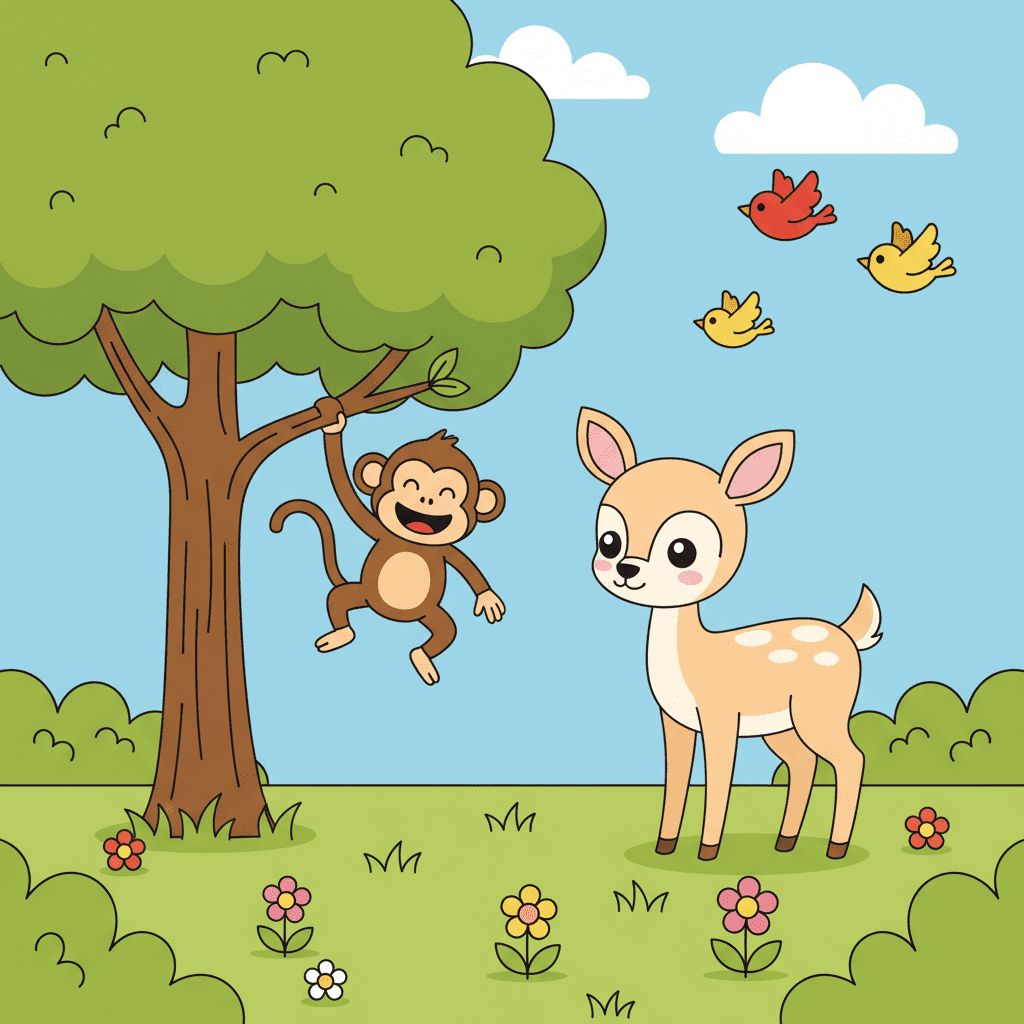
Forest Habitat
A forest is full of tall trees, plants, and many animals. Forests can be hot or cold, depending on where they are.
Animals such as deer, monkeys, snakes, owls, and insects live in forests. Trees give them food and shelter. Some animals live on the ground, while others live on branches or inside tree trunks.
Plants in forests grow tall because they compete for sunlight. The forest floor is covered with leaves, soil, and roots.
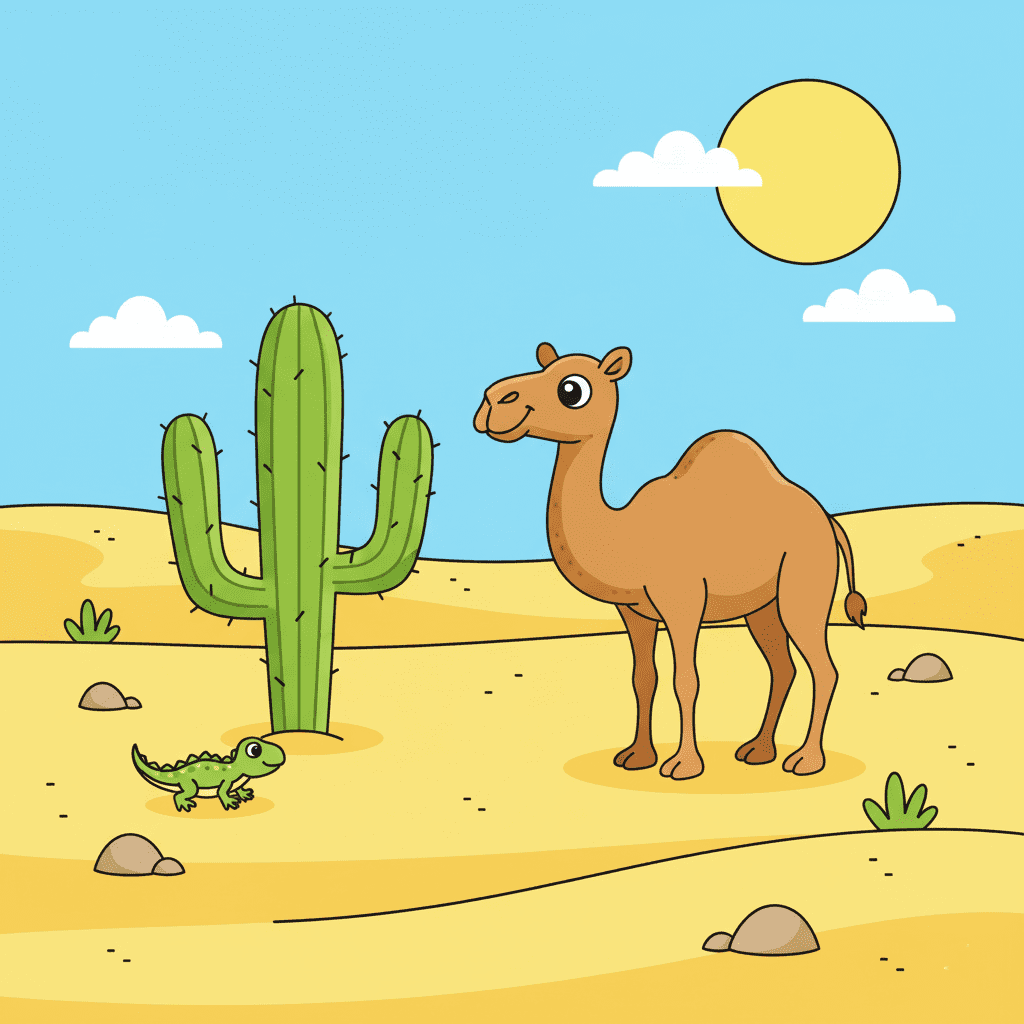
Desert Habitat
A desert is a hot and dry place. It doesn’t get much rain, and there are only a few plants. The most common plant is the cactus, which stores water in its thick stem.
Animals such as camels, snakes, lizards, and scorpions live in deserts. These animals can survive with little water. Camels, for example, have humps to store fat and can go for many days without drinking water.
Desert animals usually come out at night when it’s cooler.
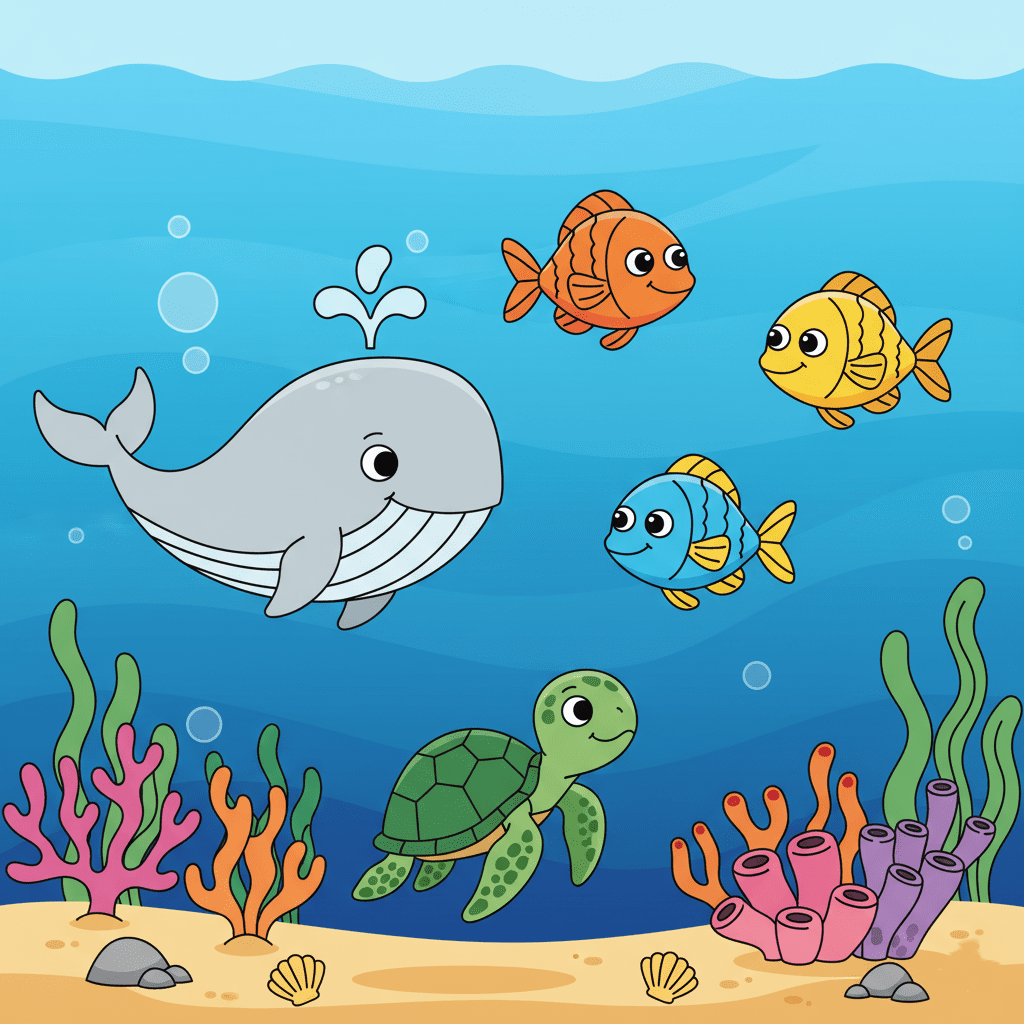
Ocean Habitat
The ocean is the largest habitat on Earth. It is home to many sea creatures like fish, whales, dolphins, sea turtles, jellyfish, and coral.
Ocean plants such as seaweeds and corals grow underwater and provide food and shelter to marine animals.
The ocean has different layers—from shallow waters near the beach to deep dark areas where sunlight cannot reach. Some animals can live only in certain parts of the ocean.
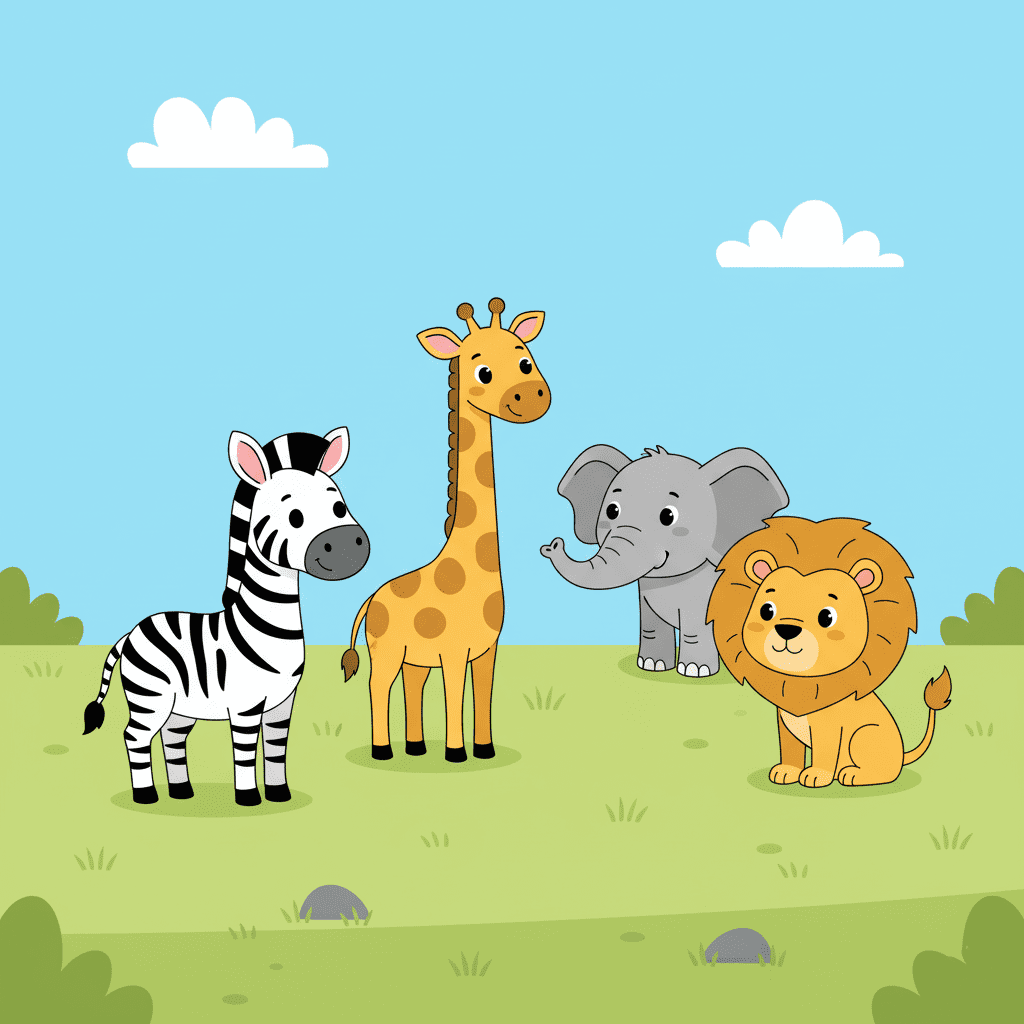
Grassland Habitat
Grasslands are wide, open spaces covered mostly with grass. The weather is usually warm, and there are only a few trees.
Animals such as zebras, lions, elephants, giraffes, and rabbits live in grasslands. They depend on grass and small plants for food.
Grasslands are often called the “home of grazers” because many animals eat grass.
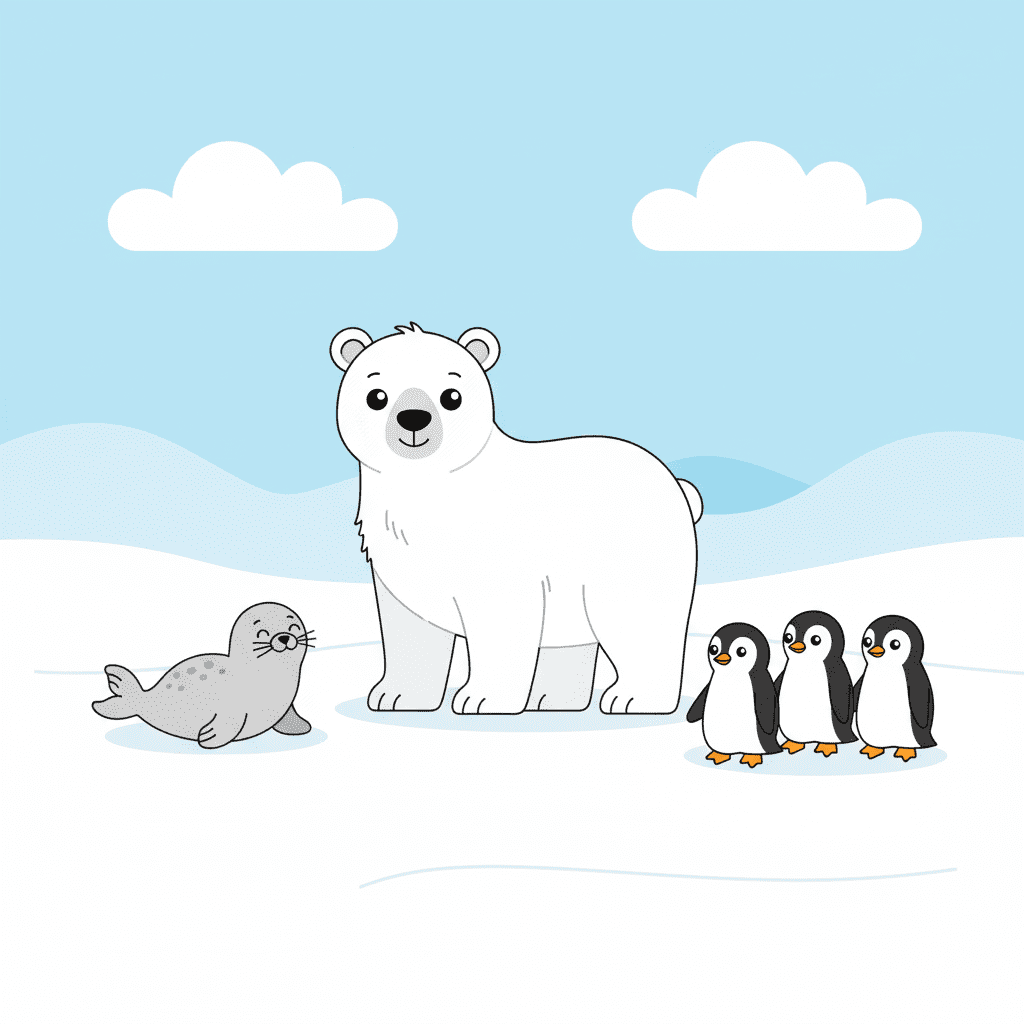
Arctic Habitat
The Arctic is a very cold and snowy habitat found near the North and South Poles. It is covered with ice most of the year.
Animals like polar bears, seals, penguins, and Arctic foxes live here. They have thick fur or fat called blubber to keep them warm. Plants like mosses and lichens can grow even in the freezing cold.
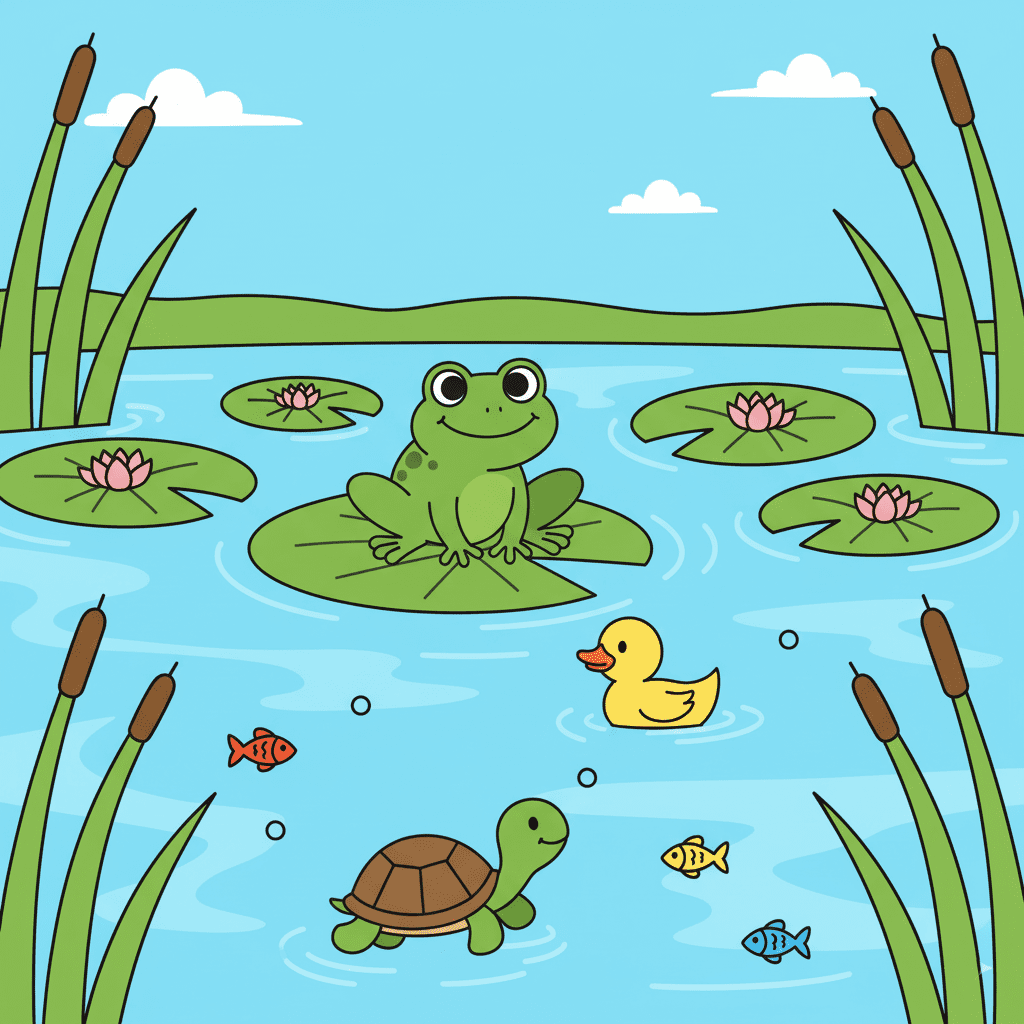
Freshwater Habitat
A freshwater habitat includes rivers, lakes, ponds, and streams. The water is not salty like the ocean.
Animals like frogs, fish, ducks, and turtles live in freshwater. Plants such as water lilies and reeds grow along the edges and provide shelter to small creatures.
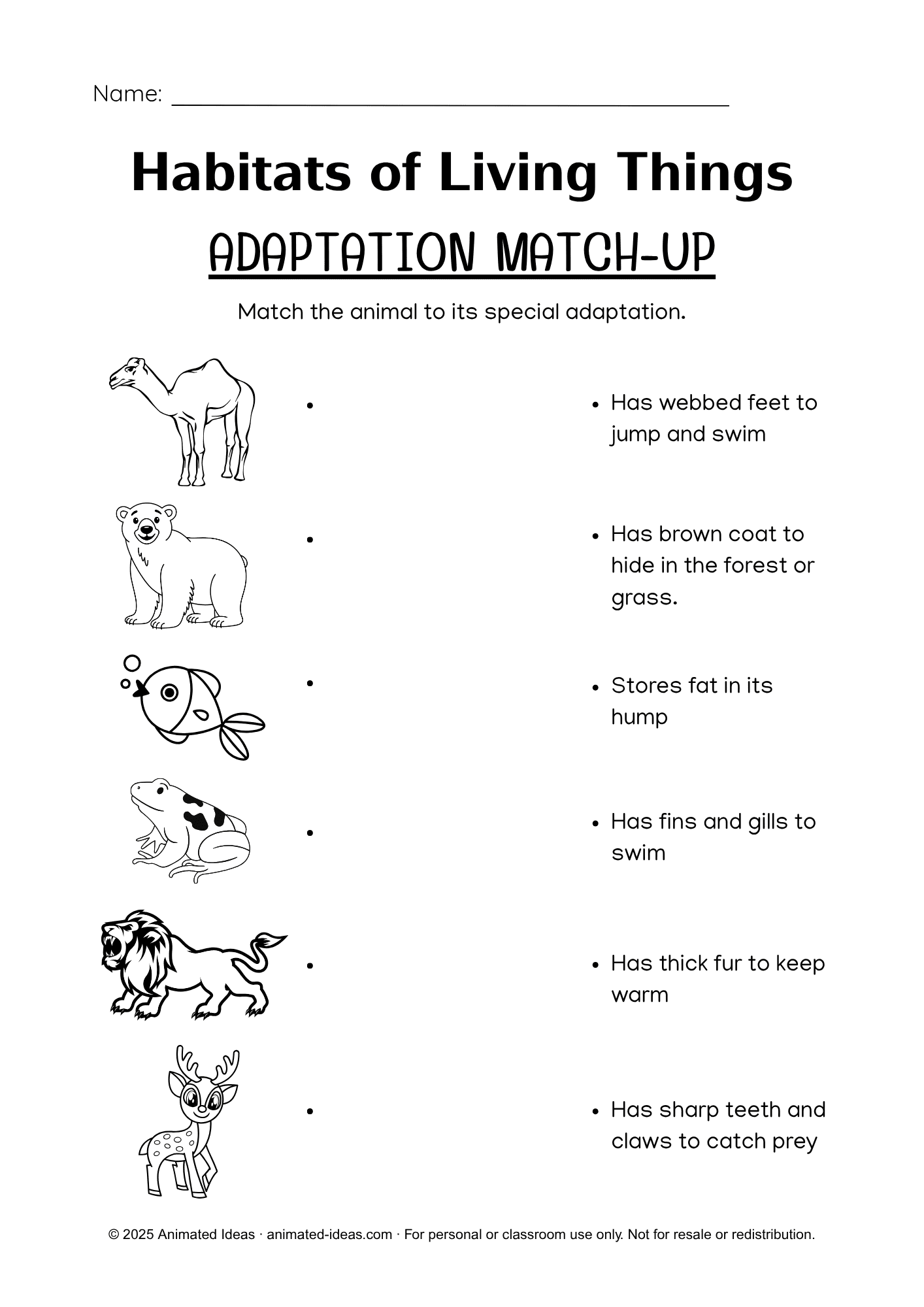
How Living Things Adapt to Their Habitats
Each living thing has special adaptations that help it survive in its habitat:
- Camel 🐪 → Stores fat in its hump
- Polar Bear 🐻 → Has thick fur to keep warm
- Fish 🐟 → Has fins and gills to swim
- Frog 🐸 → Has webbed feet to jump and swim
- Lion 🦁 → Sharp teeth and claws to catch prey
- Giraffe 🦒 → Long neck to reach leaves high in trees
- Penguin 🐧 → Flippers to swim underwater
- Duck 🦆 → Webbed feet to swim easily
These adaptations make sure that animals and plants can live comfortably in their homes.
Summary
Habitats are the homes of living things. Each habitat—forest, desert, ocean, grassland, Arctic, and freshwater—has its own weather, plants, and animals. Every living thing has special features that help it live in its habitat. We should protect these habitats to keep our planet healthy and full of life.
Thank you for reading this lesson guide about Habitats of Living Things. For more engaging resources, you can explore related topics from Animated Ideas, such as Living and Nonliving Things, Describing Natural Events With Our Senses, and all worksheets available from Animated Ideas. You can also find helpful videos and activities on my YouTube channel, stay updated with posts on Facebook, and discover more teaching materials on Pinterest.