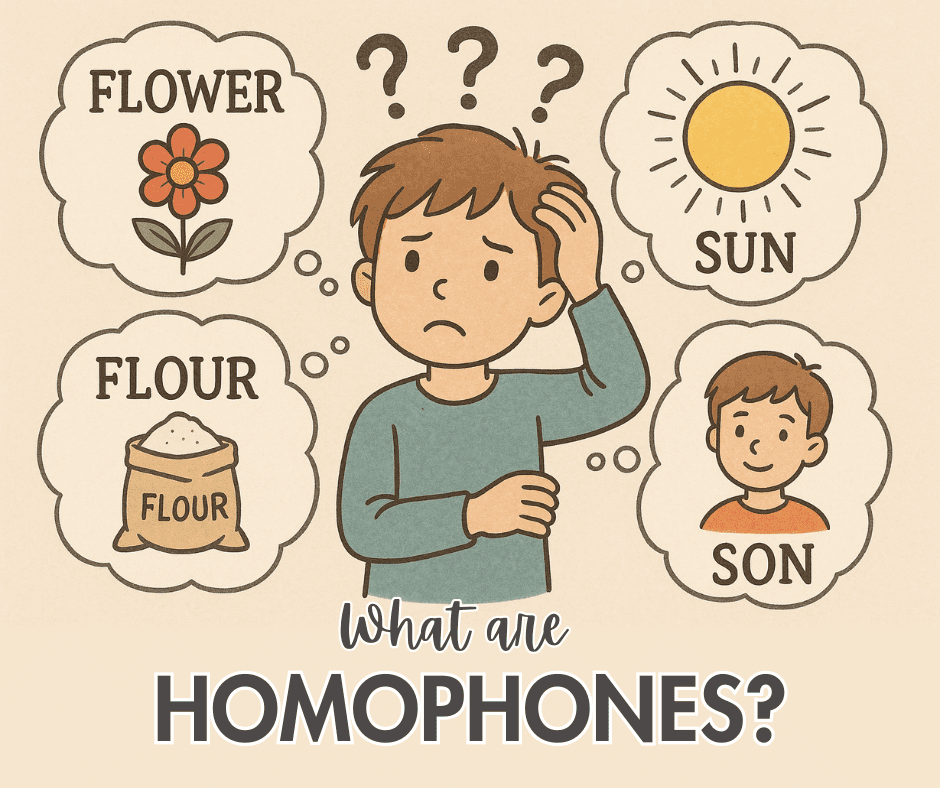
What Are Homophones?
Have you ever seen two English words that sound the same but have different meanings? These words are called homophones, and they can be tricky for many English learners. For example, “two,” “too,” and “to” all sound alike, but we use them in different ways.
Homophones are common in everyday English, and knowing them can help you speak and write more clearly. When you understand homophones, you can avoid mistakes, especially in spelling and sentence writing. This guide will explain what homophones are, show you easy examples, and give simple tips to help you remember them.
Whether you are a beginner or reviewing English basics, this lesson will make learning homophones fun, practical, and easy to understand. Let’s explore how these sound-alike words work!

Understanding Homophones in Simple Words
Homophones are words that sound the same but have different meanings and different spellings. The word comes from two Greek parts: “homo” meaning same and “phone” meaning sound. So, homophones are “same-sound” words.
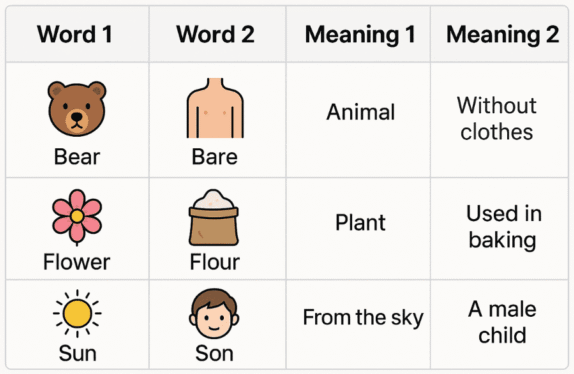
For example, when you say “flower” and “flour,” they sound alike, but one is a plant and the other is used for baking. This can be confusing for English learners, especially when reading and writing.
Homophones are common in everyday conversation, stories, school lessons, and even in jokes. This is why it is helpful to learn them early. When you know the meaning of each word, you can understand English more easily and avoid mixing up words that only sound the same.
Common Examples of Homophones
Now that you understand what homophones are, let’s look at some common examples you may see in everyday English. These word pairs sound the same, but they have different meanings and spellings. Learning them will help you avoid mistakes when reading and writing.
Here are a few simple examples:
- Right / Write
Right means correct or a direction, while write means to put words on paper. - Sea / See
Sea refers to a large body of water, and see means to look at something. - Two / Too / To
All three sound the same. Two is a number, too means “also” or “very,” and to is a preposition used in many sentences. - Meet / Meat
Meet means to come together, while meat is food from animals. - One / Won
One is a number, and won means you were the winner.
These examples show why paying attention to spelling is important. Even small mistakes can change the meaning of your sentence completely. In the next part of this lesson, we will look at easy tips to help you remember homophones and use them correctly.
Download Free Worksheets and Quiz
Worksheets are still a great way to reinforce what you have learned. You can use printables with:
- Fill-in-the-blank sentences
- Word-picture matching
- Short correction tasks
It helps bring everything together.
If you’d like a free homophones worksheets, you can download it below. Or feel free to browse our library of resources to find more worksheets that suit your needs.
More Homophones in Sentences
Here are more common homophones with example sentences to help you understand their meanings and how to use them correctly in everyday English.
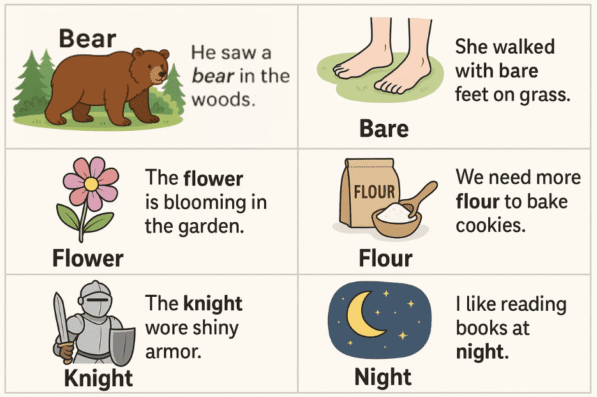
Flower / Flour
- The garden has a beautiful flower.
- I need flour to bake a cake.
Bear / Bare
- We saw a bear in the forest.
- He walked on the sand with bare feet.
Blue / Blew
- The sky is blue today.
- The wind blew the leaves off the tree.
Mail / Male
- I received a letter in the mail.
- The male cat is sleeping in the sun.
Pair / Pear
- I bought a pair of shoes.
- I ate a juicy pear for snack.
Hear / Here
- I can hear the birds singing.
- Please come here and help me.
A Beginner-Friendly Homophones List
To help you learn homophones quickly, here is a small list of additional common homophones with their meanings.
- Brake / Break – Brake: to stop a vehicle; Break: to separate into pieces.
- Cell / Sell – Cell: a small room or basic unit of life; Sell: to give something in exchange for money.
- Plain / Plane – Plain: simple or clear; Plane: an aircraft or flat surface.
- Weak / Week – Weak: not strong; Week: a period of seven days.
- Sight / Site – Sight: the ability to see; Site: a place or location.
- Right / Rite / Write – Right: correct; Rite: a ceremony; Write: to put words on paper.
- Fair / Fare – Fair: just or light in color; Fare: the price of a ticket.
- Die / Dye – Die: to stop living; Dye: a substance used to change color.
- Road / Rode – Road: a street or path; Rode: past tense of ride.
- Hair / Hare – Hair: grows on your head; Hare: a fast animal similar to a rabbit.
Here are a few more simple sentences using homophones to help you understand their meanings in real-life contexts.
- The knight saw the moon at night.
- She knew I had a new bike.
This not only makes you giggle, but it helps you use the words correctly in everyday situations.

Tips for Remembering Homophones Easily
Homophones—words that sound the same but have different meanings and spellings—can be tricky for beginners. But don’t worry! With some simple strategies and regular practice, you can master them and use them confidently. Here are some practical tips to help you remember homophones more easily:
1. Use Short Sentences to Practice
Writing simple sentences for each homophone helps you understand how they are used in real situations. Sentences give context, which makes it easier to remember the correct spelling.
Try to create your own sentences using the homophones you learn. This personal connection will help the words stick in your memory.
2. Look at Pictures or Charts
Visual aids make learning more interesting and effective. You can draw simple pictures or create charts that show the differences between homophones.
Example:
| Word | Meaning | Picture Idea |
|---|---|---|
| sea | large body of water | waves in the ocean |
| see | to look at something | eyes looking |
3. Read Often
Reading regularly exposes you to homophones in different contexts, helping you see how they are used correctly. Over time, your brain will start to remember the correct spelling automatically.
Suggested reading materials for beginners:
- Children’s books or short stories
- Simple news articles online
- English learning blogs and worksheets
Tip: While reading, underline or highlight homophones you notice and try to write your own sentences with them later.
4. Practice with Games and Quizzes
Learning doesn’t have to be boring! Playing games like matching homophones, fill-in-the-blank exercises, or online quizzes can make practice fun and effective.
5. Review Regularly
Repetition is key. Review the homophones you’ve learned every week to make sure they stay fresh in your memory. The more you practice, the easier it will become to spell and use them correctly.
By using these tips, you can master homophones step by step.
Conclusion
Homophones are words that sound the same but have different meanings and spellings. Learning them can be tricky at first, but with consistent practice, reading, and the use of tips like visual aids, sentence exercises, and memory clues, anyone can master them. Understanding homophones improves your writing, speaking, and overall English skills.
By practicing regularly and using simple strategies, you can avoid common mistakes and gain confidence in using the right words in the right context.